When choosing a compressed air dryer for your pneumatic application, it is important to understand the benefits and downfalls of the different drying technologies available.
In this article:
- Comparing the Technologies: A Glance
- Desiccant Regenerative Dryers: Explained
- Refrigerant Dryers: Explained
In the market for a compressed air dryer?
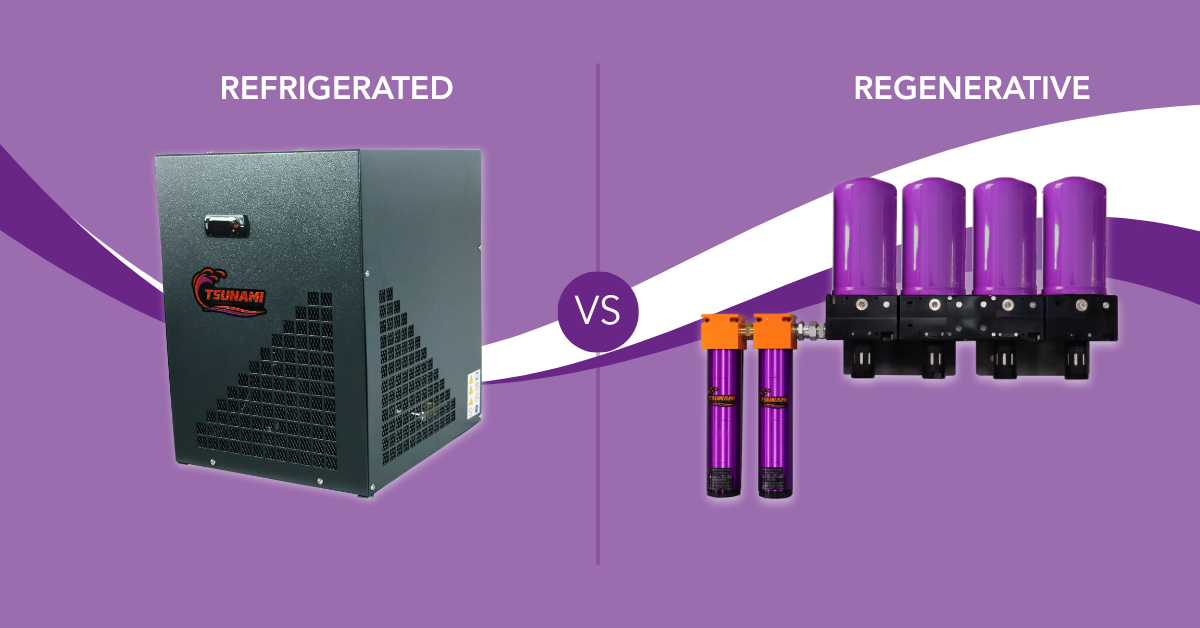
When selecting a compressed air dryer for your pneumatic application, it is essential to possess a thorough knowledge of the various drying technologies at your disposal. While all dryers offer some level of effectiveness and value, the specific type that best suits your needs will depend on the desired performance.
Comparing the technologies: a glance
Regenerative Dryers
- Delivers ultra-low dew points (as low as -80°F)
- Designed for critical applications requiring extremely dry air
- Available in electric or fully pneumatic (C1D1) models
- Includes multi-stage filtration fir maximum air quality
- More robust moisture removal for precision or sensitive processes
Refrigerant Dryers
- Ideal for general-purpose compressed air systems
- Consistent dew points 38-50°F
- Lower upfront cost compared to regenerative systems
- Simple installation and low maintenance
- Best for non-critical application where ultra-low dew point is not required
Desiccant Regenerative Dryers: Explained
Regenerative dryers use multiple canisters of desiccant to remove water vapor from compressed air. As compressed air flows through a desiccant canister, providing dry air downstream, a separate pilot signal is sent to one or more of the other desiccant canisters to discharge the pressure inside.
While this is occurring, a regeneration orifice allows some of the very dry air to flow back through the media so that the dry air can “sweep” away the water vapor that canister removed during its drying period. This effectively dries the media so it is ready to remove more water vapor when the tower comes online again for the drying process.
This process of switching back and forth to dry the desiccant towers is called the regeneration cycle. In a nutshell, it’s like replacing your desiccant beads every couple of minutes.
Refrigerant Dryers: Explained
 Refrigerant air dryers work similarly to your refrigerator or freezer at home. Air enters a heat exchanger where it is physically cooled in an air-to-refrigerant heat exchange unit; the process essentially cools the air until it reaches the temperature setting (dew point) of the refrigerant dryer.
Refrigerant air dryers work similarly to your refrigerator or freezer at home. Air enters a heat exchanger where it is physically cooled in an air-to-refrigerant heat exchange unit; the process essentially cools the air until it reaches the temperature setting (dew point) of the refrigerant dryer.
The water condenses out of the air stream and is removed as the dry air exits the dryer and goes through a water separation filter. A refrigerated dryer is a must in any operation, facility, or application that requires compressed air and is used regularly to help protect your equipment in the long-term.
Unfortunately, hot summer temps and high surges in air demand will greatly limit performance and can dramatically impact the air quality being provided to your air system.
Pros & Trade-offs
Both dryers offer simple operation, easy, infrequent maintenance, and increase the productivity of any long-lasting operation; but depending on what your facility looks like, one drying system may work better over the other. Here are some things to consider when making your decision:
Regenerative Air Dryers
Advantages:
- Deep dryer performance (low dew points)
- Handles hot high surges and low flows well
- No refrigerant handling
Trade-offs:
- Requires filters & periodic maintenance
- Slight loss of compressed air during regeneration
Refrigerant Air Dryers
Advantages:
- Simple operation with a common setup
- Good default option for moderate conditions
Trade-offs:
- Less effective under surge/flow
- Limited dew points
- Requires refrigerant handling and regular servicing
Which air dryer is right for you?
Ultimately, the best air dryer depends on your application, environment, and system needs. Regenerative dryers offer extremely low dew points and are ideal for demanding or sensitive processes. Refrigerant dryers, on the other hand, are reliable and energy-efficient for general-purpose drying in controlled environments.
At Tsunami Compressed Air, we offer both technologies because we know there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Whether you need ultra-dry air for precision work or an efficient option for everyday operations, our team can help you find the right fit.
Updated on 07/15/2025 for clarity and accuracy.